Engineering Spec 01: Authentication and Authorization Flow
Changelog
Current version: v2.
Changes in v2:
- Remapped PKCE authentication into a simpler implementation of JWT key pair to keep it simple.
- Added some details on where the JWT key pair shall be placed.
Summary
This engineering specification concerns the full flow of authentication and authorization for the app, is subjected to changes at any time during the iterative process.
To recap, authentication section will concern the process of registering and logging in, and how to properly save the user credentials as well as what to do to adhere to OWASP best practices. Authorization section will concern the process of validating and granting permissions to permitted resources after logging in succeeded.
User Flow
High-level user flow for the requirement to use “JWT Access Key / Secret Key” as a mechanism.
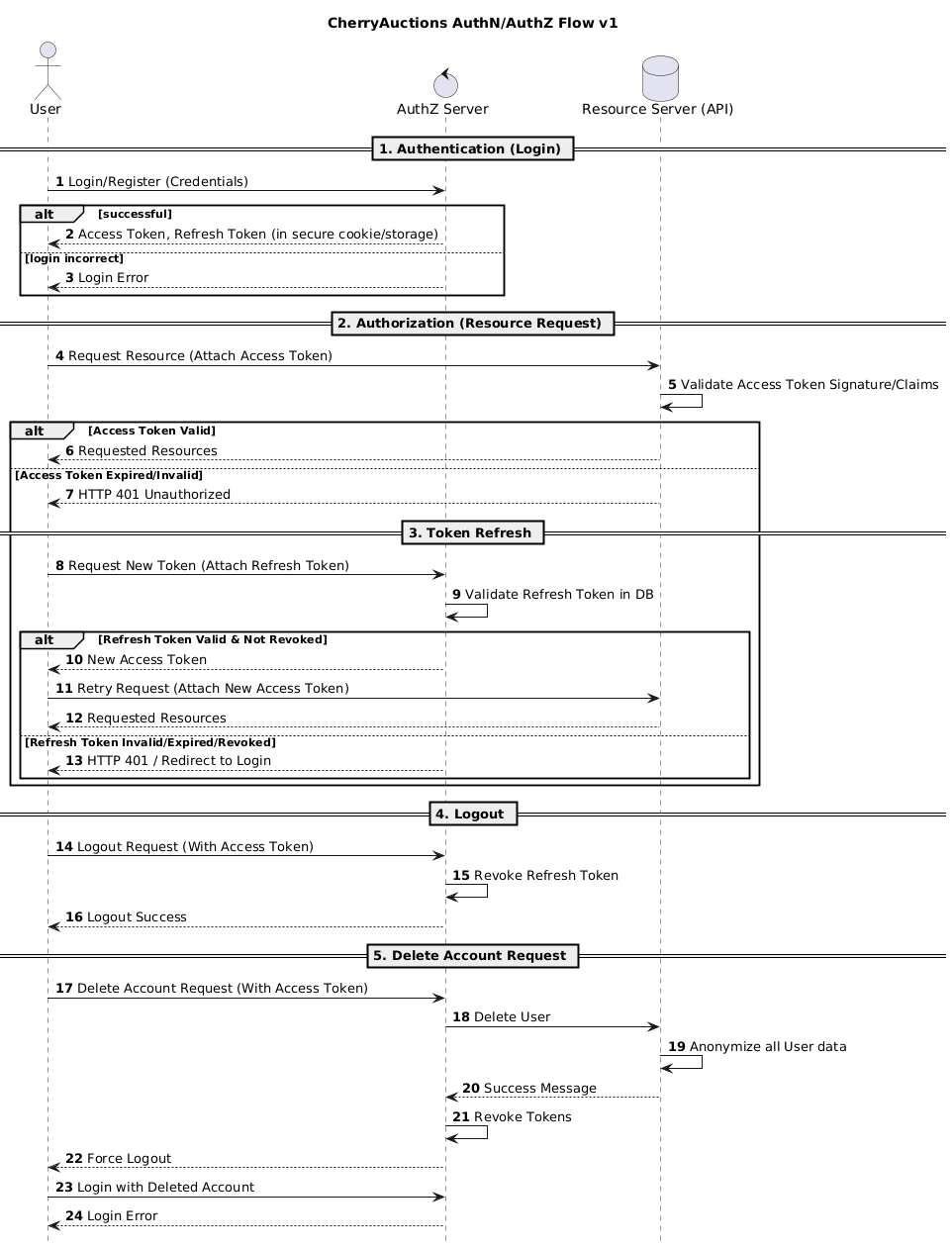
Authentication and Authorization
Overview:
- All endpoints must adhere to standards provided by REST API Standards, such as GET endpoints are always idempotent and should never have any side effects or business operations on the server side.
- All endpoints are named properly after the resources they revolve around.
- Error codes should be returned, with an optional error description, but don’t prioritize error description as it should integrate with I18n.
Authentication
Authentication is carried out by checking the Authorization header in requests for Bearer-type tokens. The access_token retrieved from registration and login endpoints must be used here, refresh_token only serves as a way to rotate and gain a new access token.
The RefreshToken lives as a HttpOnly cookie, with a month-long expire duration.
Registration
Each user is registered with a unique email address, with a name that is optional, as every authentication should be done via the email address (whether retrieved from Google or inputted directly).
- Endpoint
/v1/auth/register. - Accepts
application/json. - Must return an
access_tokenand arefresh_token.
This format can be changed to a PKCE flow as outlined in the legacy authentication authorization document, but there is currently no plan to support other devices, such as native, other REST clients or servers.
Logging in
Each user can login to the system with their email address with the password, or use one of the OAuth providers.
- Endpoint
/v1/auth/login. - Accepts
application/json. - Must return an
access_tokenand arefresh_token.
Refresh
Refreshing takes the RefreshToken cookie, and checks against the database if the refresh token has been revoked or not. It grants a new access token, and optionally rotate the refresh token (up to the implementer) with a new Set-Cookie if it is a valid token. Otherwise, this clears the cookie and returns 401 unauthorized.
Logout
Logging out instantly invalidates a refresh token.
Notice: Frontend must be wary to remove the access token from memory given the user’s logout request.